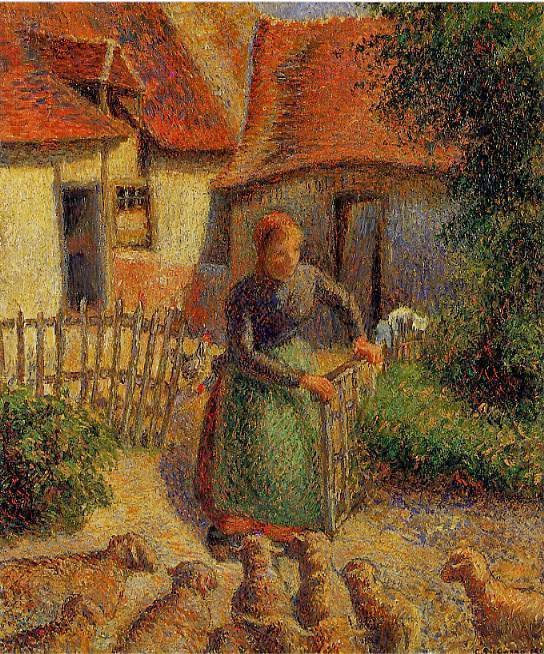In December it was announced that the University of Oklahoma and Leone Meyer had reached a tentative settlement in the litigation over Meyer’s claims to La Begère by Camille Pissarro, a painting stolen from her father Raoul during the Vichy regime. Yesterday the final agreement was made public. As reported by Graham Bowley at the New York Times, title to the painting will reportedly be confirmed as Meyer’s, and the work will be displayed on a rotating basis in France (where Meyer lives) and the Fred Jones, Jr. Museum of Art (where it has been) until such time as Meyer donates it to a French museum (either during life or in her will). It is a remarkable development in a case that the Oklahoma defendants defended vigorously, and a credit to the participants and lawyers involved on both sides that they were able to bridge the gap and reach an agreement.
Léone Meyer and University of Oklahoma Settle Nazi-looted Pissarro Dispute
Topics: Léone Meyer’s, University of Oklahoma, Fred Jones Jr. Museum of Art, Restitution, World War II, Camille Pissarro
U.S. Museums and Looted Art—Is it Whether you Win or How you Play?
A recent report by the World Jewish Restitution Organization (WJRO) has made strong criticisms of American museums with respect to their handling of Nazi-looted art claims. In particular, the report criticizes the assertion of timeliness defenses such as statutes of limitations. The report focuses in particular on cases involving the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, the Norton Simon Museum in Pasadena, the Toledo Museum of Art, and the Fred Jones, Jr. Museum at the University of Oklahoma. There is no state control over the vast proportion of art in America the way there is in most European countries, and thus, no possibility of singular, nationalized approaches. In response to the report, some of the museums mentioned have defended their strategies, though in some cases the players are talking past each other. What is undeniable is that whether as a function of the nature of U.S. museums (largely private, rather than public), it is hard to say there is a coordinated approach to the issue, good or bad. The report is lengthy and detailed, and well worth a read in depth that space here does not permit. In some ways, the question it poses boils down to this: is determining the historical truth the obligation of everyone involved or is there some room to prevail without addressing the larger issues?
Topics: Toledo Museum of Art, Street Scene in Tahiti, Léone Meyer’s, American Association of Museums, Two Nudes, La bérgère, AAMD Task Force on the Spoliation of Art during th, Thyssen-Bornemisza Collection, Rue St. Honoré après-midi êffet de pluie, University of Oklahoma, Cassirer, Nazi-looted art, Washington Conference on Holocaust Era Assets, Fred Jones Jr. Museum, Washington Principles on Nazi-Confiscated Art, World Jewish Restitution Organization, WJRO, Association of Art Museum Directors, Restitution, American Alliance of Museums AAM, World War II, Paul Gaugin, Camille Pissarro, Oskar Kokoschka, Museums, Museum of Fine Arts Boston, AAMD, Norton Simon Museum in Pasadena